Introduction: Understanding Congruence in Mathematics
When we first encounter the term “congruent” in mathematics, it might seem like a complicated concept. However, it’s actually a straightforward idea that plays a crucial role in geometry, algebra, and even number theory. So, what does “congruent” really mean?
In simple terms, congruent refers to objects that are identical in shape and size. In math, this concept is often applied to figures or numbers that can be transformed into each other through translations, rotations, or reflections. Whether you’re dealing with triangles, angles, or numbers, understanding congruence is essential to mastering many mathematical principles.
In this article, we’ll explore the meaning of congruent in mathematics, how it applies to various mathematical fields, and how to recognize congruent objects.
What Does Congruent Mean in Mathematics?
In mathematics, congruence means that two objects or figures are exactly the same in terms of size and shape. However, this doesn’t always mean that the objects must be in the exact same location or orientation. For example, two shapes might be congruent even if one is rotated or flipped compared to the other.
Congruence in Geometry
One of the most common areas where we use the concept of congruence is in geometry. Congruent figures in geometry are shapes that can be made to overlap exactly by a series of transformations like translations, rotations, and reflections.
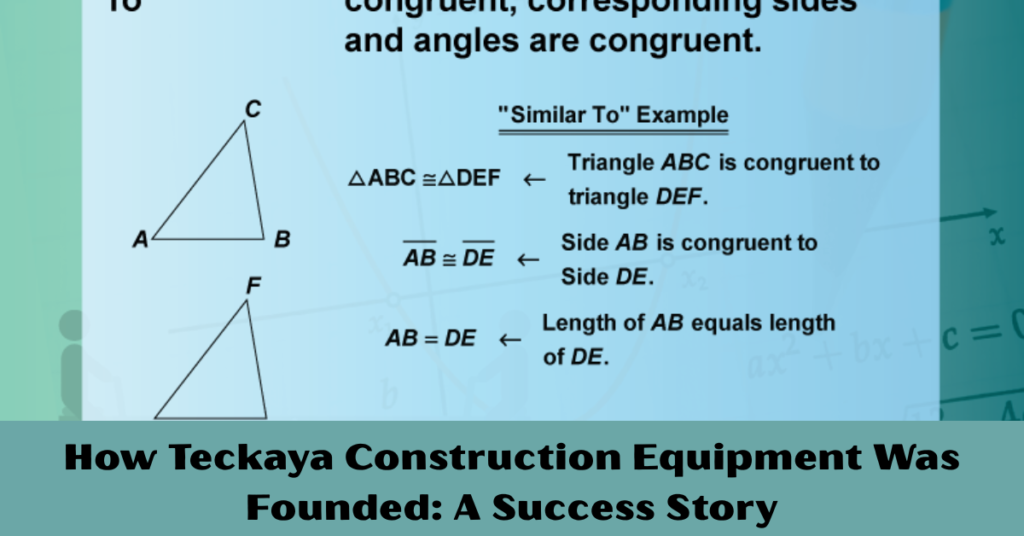
For example, two triangles are congruent if they have:
-
The same side lengths.
-
The same angles.
This is expressed using the congruence symbol (≅). When two geometric figures are congruent, we can say:
-
Triangle ABC ≅ Triangle DEF (This means both triangles have the same size and shape.)
Congruence of Angles
In addition to shapes, angles can also be congruent. Two angles are congruent if they have the same measure, regardless of their orientation. For example, if angle A is 45°, and angle B is also 45°, then angle A ≅ angle B.
Congruence of Numbers
Congruence isn’t just restricted to shapes and angles. In number theory, congruence is used to describe numbers that have the same remainder when divided by a particular number. This is often referred to as modular arithmetic.
For example, we can say:
-
7 ≡ 2 (mod 5)
This means that when 7 and 2 are divided by 5, both leave a remainder of 2, making them congruent modulo 5.
How to Recognize Congruent Figures
Recognizing congruent figures in mathematics is key to solving various problems, especially in geometry. Here are some ways to check if two figures are congruent:
1. Check Side Lengths and Angles
-
For polygons like triangles and quadrilaterals, ensure that corresponding sides and angles are equal.
-
For circles, check that both have the same radius.
2. Use Transformations
You can often prove congruence by trying to map one figure onto the other using translations (sliding), rotations (turning), or reflections (flipping).
Examples of Congruence in Mathematics
To make the concept of congruence clearer, let’s look at a couple of examples:
Example 1: Congruent Triangles
Imagine two triangles, one labeled ABC and the other labeled DEF. If triangle ABC has sides of length 3, 4, and 5 units, and triangle DEF also has sides of length 3, 4, and 5 units, and the corresponding angles are the same, then the two triangles are congruent:
-
Triangle ABC ≅ Triangle DEF.
Example 2: Congruent Angles
Suppose we have two angles, angle P and angle Q. If both angles measure 60°, we can say:
-
Angle P ≅ Angle Q.
Example 3: Modular Congruence
In modular arithmetic, we can say that 12 and 17 are congruent modulo 5, because when divided by 5, both leave a remainder of 2:
-
12 ≡ 17 (mod 5).
FAQs About Congruence in Mathematics
What does it mean for two shapes to be congruent?
Two shapes are congruent if they have the same size and shape, and they can be made to overlap perfectly by using transformations such as translation, rotation, or reflection.
How do you prove that two triangles are congruent?
To prove two triangles are congruent, you can use criteria like SSS (Side-Side-Side), SAS (Side-Angle-Side), or ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), which compare the side lengths and angles of the triangles.
Is congruence the same as equality?
While both congruence and equality mean “the same,” congruence is more often used for geometric shapes and angles, while equality refers to numbers, expressions, or quantities.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Congruence
Understanding congruence in mathematics is fundamental to solving problems in geometry, algebra, and number theory. Whether it’s comparing shapes, angles, or numbers, knowing how to identify congruent objects will help you tackle more complex mathematical problems with ease.
If you found this explanation helpful, you can dive deeper into related topics like transformations, geometric proofs, or modular arithmetic to enhance your understanding of mathematics even further.